Invented by David John King, Alison Witte, Heidi N. LeBlanc, Richard Theolis, Asna Masood, Mark Yamanaka, Kyra D. Zens, Sarah R. Reed, Tim Sproul, Chetana Rao-Naik, David Passmore, Dawn M. Tanamachi, Kristopher Toy, ER Squibb and Sons LLC
The market for human antibodies that bind to CD22 is growing rapidly, with a number of pharmaceutical companies investing in research and development in this area. One of the main uses of these antibodies is in the treatment of B cell malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. These diseases are characterized by the abnormal growth and proliferation of B cells, and human antibodies that bind to CD22 can be used to target and destroy these cells.
In addition to their use in cancer treatment, human antibodies that bind to CD22 are also being investigated for their potential use in treating autoimmune disorders. These diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues in the body, and targeting CD22 can help to regulate the activity of B cells and prevent them from attacking healthy tissues. Some of the autoimmune disorders that are being targeted with CD22 antibodies include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.
Another potential use for human antibodies that bind to CD22 is in the treatment of transplant rejection. When a person receives an organ transplant, their immune system may recognize the transplanted tissue as foreign and attack it. By targeting CD22, human antibodies can help to suppress the activity of B cells and prevent them from attacking the transplanted tissue.
Overall, the market for human antibodies that bind to CD22 is expected to continue growing in the coming years, as more research is conducted and new applications for these antibodies are discovered. With their potential to treat a wide range of diseases, these antibodies represent a promising area of research and development in the field of biotechnology.
The ER Squibb and Sons LLC invention works as follows
The present disclosure provides monoclonal monoclonal antibody that binds to CD22 specifically and with high affinity. This includes human monoclonal antibody. The present disclosure also provides nucleic acids encoding antibodies, expression vectors and host cells, as well as methods of expressing antibodies. The disclosure also includes antibody-partner molecule combinations, bispecific molecules, and pharmaceutical compositions containing the antibodies. This disclosure provides methods to detect CD22 as well as treatments for cancers, inflammatory and auto-immune disorders and other diseases using an anti CD22 antibody.
Background for Human antibodies that bind to cd22 (and their uses)
Anti-CD22 Antibodies
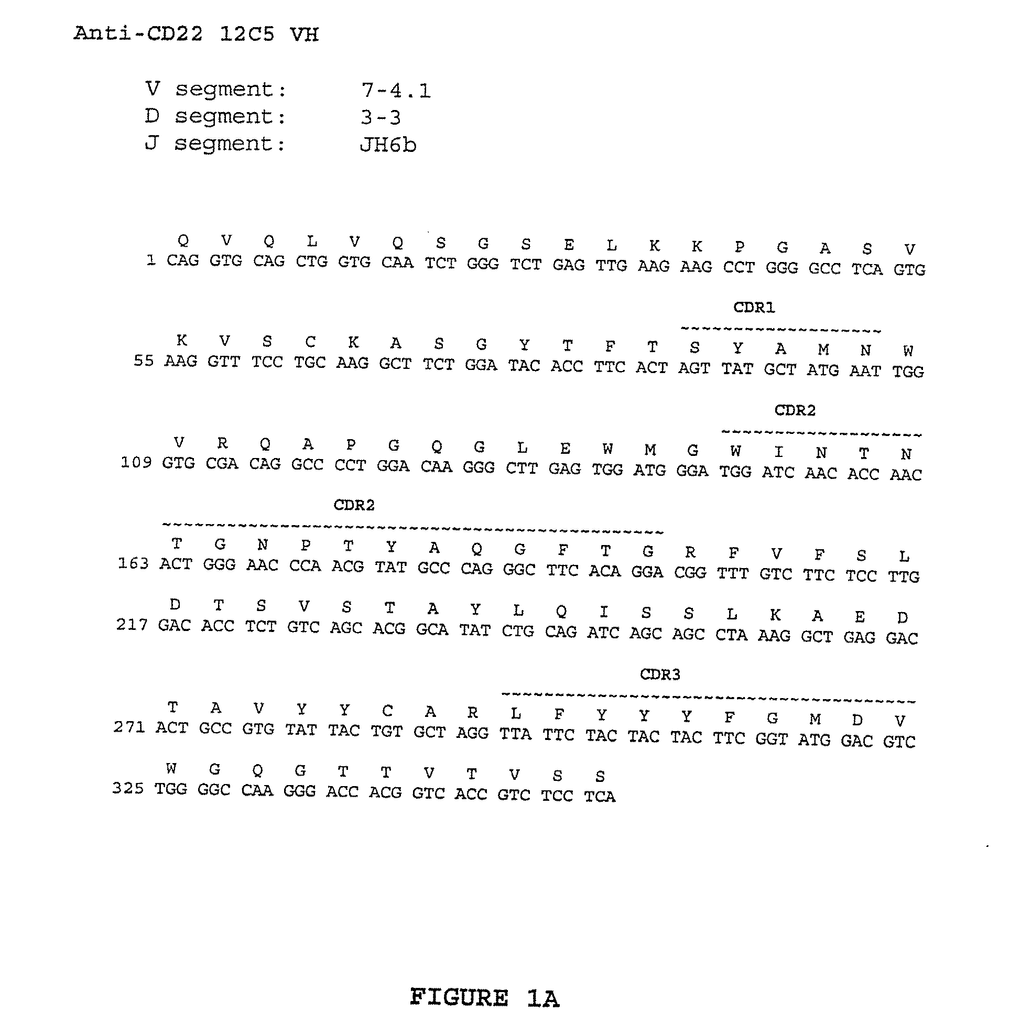
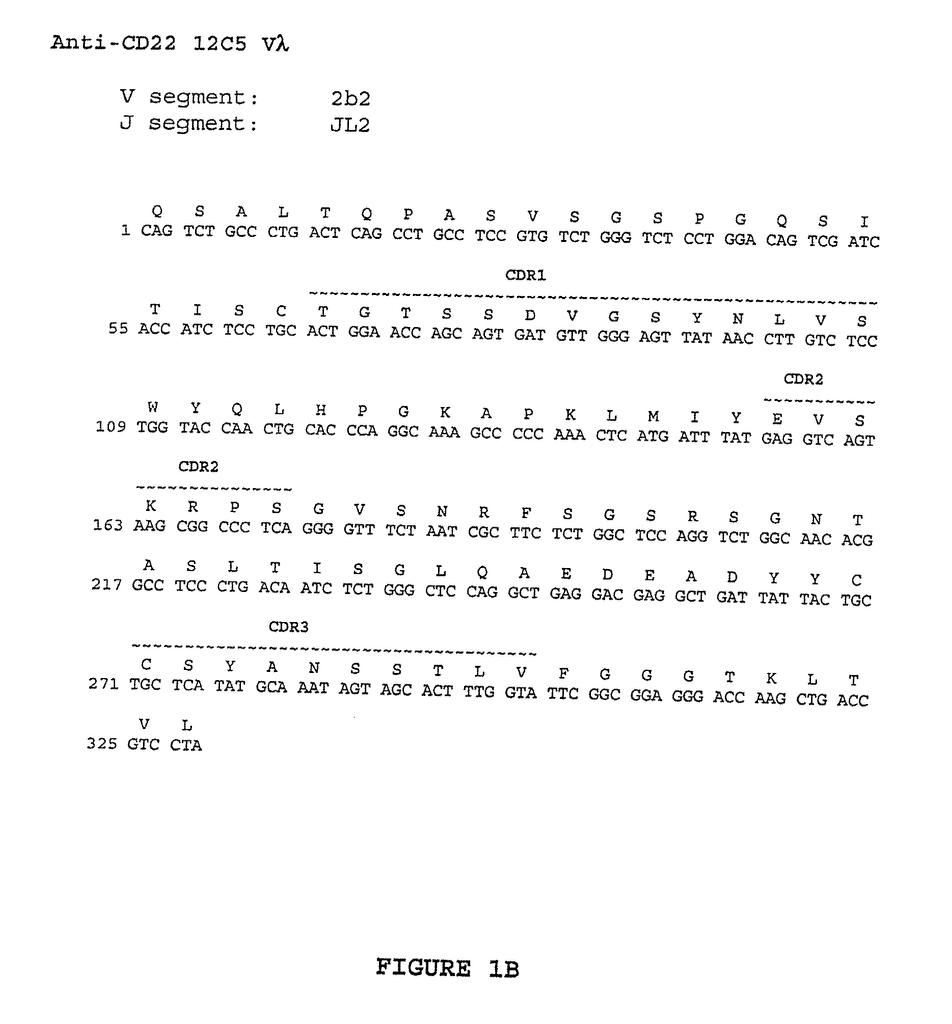
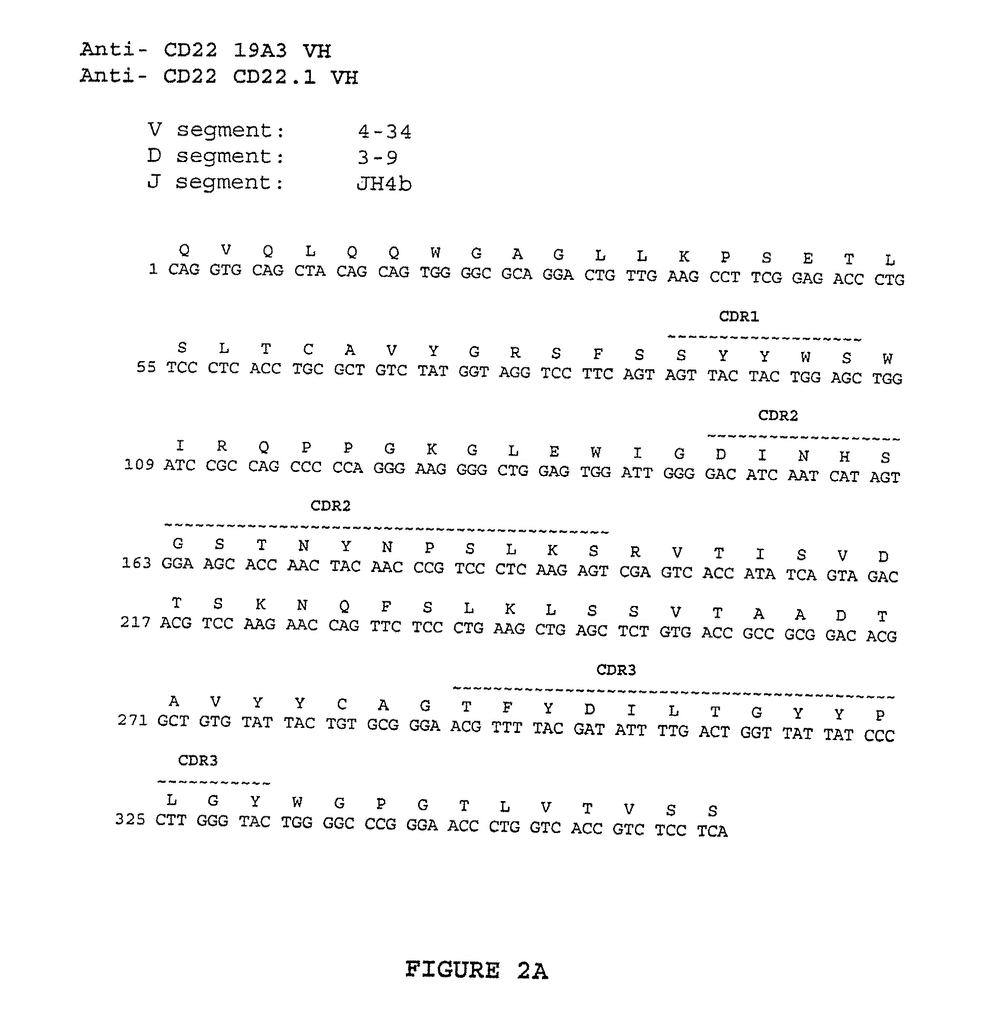
Monoclonal Antibodies 16F7, 19A3, 4G6, 21F6, 23C6, CD22.1 and CD22.2
Antibodies with Particular Germline Sequences
Homologous Antibodies
Engineered and Modified Antibodies.
Antibody Fragments” and “Antibody Mimetics”.
Antibody Physical Properties
Methods of Engineering Antibodies”.
Immunization of Human Ig Mice
Characterization Antibody Binding To Antigen
Bispecific Molecules
Linkers
Partner Molecules
Pharmaceutical Compositions
Uses and methods of the Invention”.
Example 1
Generation of Human Monoclonal Antibodies against CD22
Antigen
Mouse Strains
Immunization
Antibody Selection
Click here to view the patent on Google Patents.