Invented by Edward C. Rieker, Daniel K. Mansfield, Envoy Corp
An automated system for real-time verification of health insurance eligibility is a software that allows healthcare providers to check the eligibility of patients in real-time. This system is designed to access the patient’s insurance information and verify their eligibility for medical services. The system is easy to use, and it reduces the time and effort required to verify insurance eligibility manually.
The market for automated systems and methods for real-time verification of health insurance eligibility is driven by the increasing demand for healthcare services. As the population grows, the demand for healthcare services also increases. This has led to an increase in the number of patients seeking medical services, which has put pressure on healthcare providers to provide efficient services. Automated systems and methods for real-time verification of health insurance eligibility help healthcare providers to provide efficient services by reducing the time and effort required to verify insurance eligibility manually.
Another factor driving the market for automated systems and methods for real-time verification of health insurance eligibility is the need for accuracy. Manual verification of insurance eligibility can be prone to errors, which can lead to incorrect billing and reimbursement. Automated systems and methods for real-time verification of health insurance eligibility are designed to reduce errors and ensure accuracy in the verification process.
The market for automated systems and methods for real-time verification of health insurance eligibility is also driven by the need for cost-effectiveness. Healthcare providers are always looking for ways to reduce costs while maintaining the quality of services. Automated systems and methods for real-time verification of health insurance eligibility help healthcare providers to reduce costs by reducing the time and effort required to verify insurance eligibility manually.
In conclusion, the market for automated systems and methods for real-time verification of health insurance eligibility is growing rapidly. This is driven by the increasing demand for healthcare services, the need for accuracy, and the need for cost-effectiveness. Healthcare providers who adopt these systems and methods will be able to provide efficient services while reducing costs and ensuring accuracy in the verification process. As the market continues to grow, we can expect to see more innovative solutions that will further enhance the efficiency of healthcare services.
The Envoy Corp invention works as follows
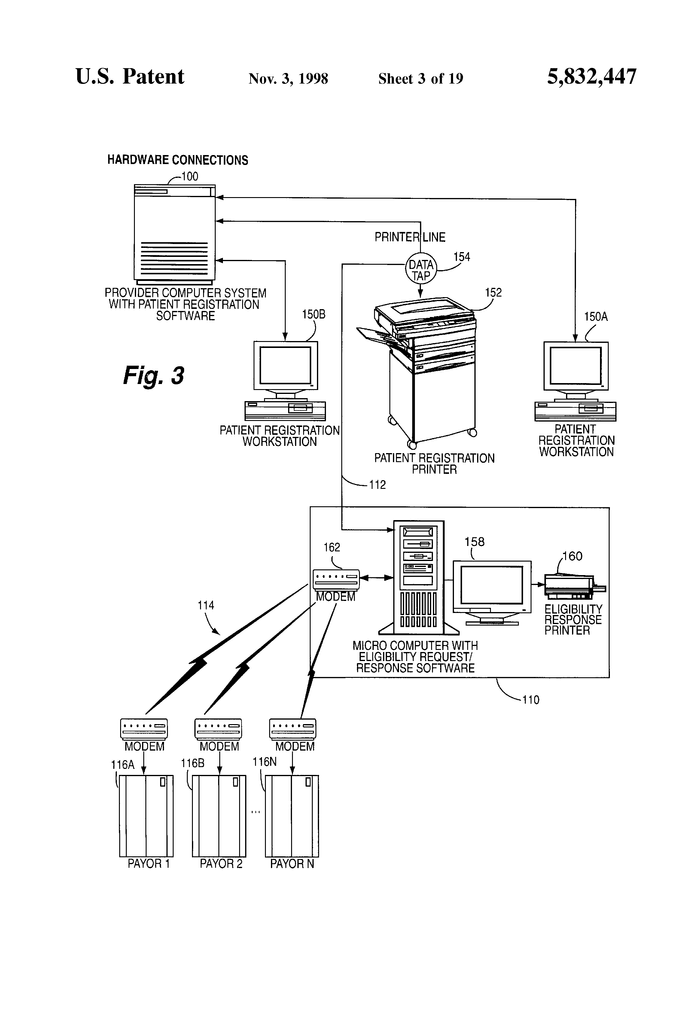
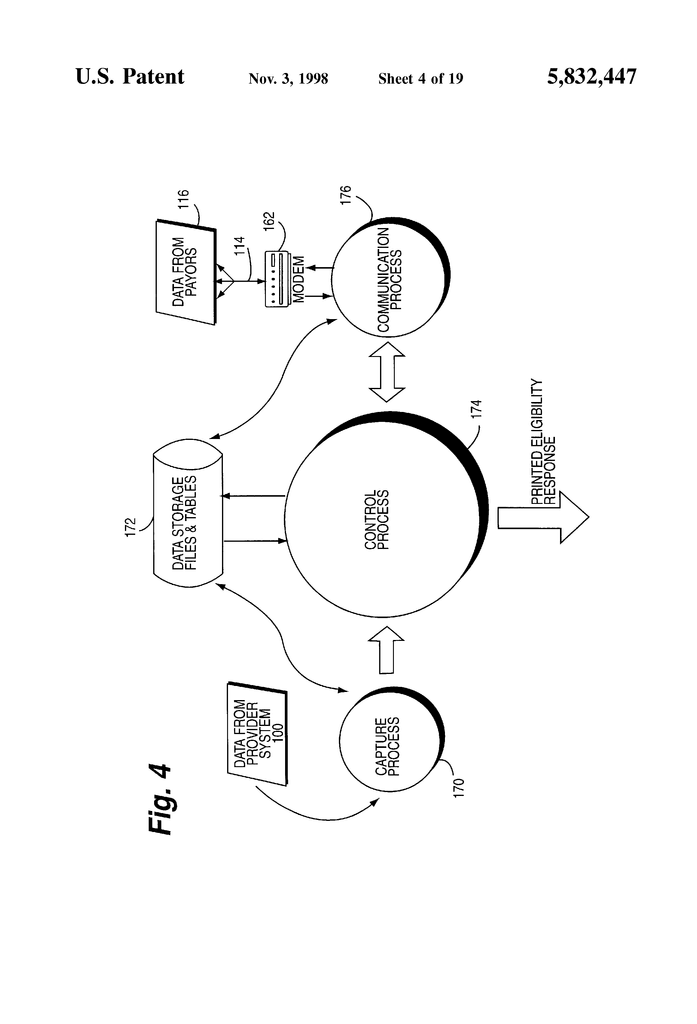
Data from the computer system of a health-care provider is used to request in real time electronic information about insurance eligibility from health insurance payors. The patient health insurance system verification computer is connected to the patient registration system. The registration computer system sends the verification computer a data stream, such as an image of a printed page. The data stream is then captured and separated into different data fields. The verification computer system determines the insurance carrier and then which electronic data sources to use for patient eligibility data. The verification computer system reformats captured data into the format demanded by the data sources, establishes the communications link with the data sources, and then sends reformatted data back to the source. The data source provides the verification computer with patient-specific eligibility data that it uses to verify insurance coverage automatically. The automatic verification of health insurance coverage is more reliable because no human interaction is needed. Automatic verification is also possible without the need for double data entry, even in environments that have pre-existing admissions software.
Background for Automated System and Method for Real-Time Verification of Health Insurance Eligibility
At the moment, hospitals and healthcare providers are having a difficult time determining if patients qualify for coverage under health insurance. The admitting staff will ask a patient if they have health insurance when they seek health care in a hospital. The admitting staff may ask for proof of insurance eligibility, such as a medical card, or similar. The hospital’s computerized admissions system inputs the information corresponding to any health insurance that the patient claims to have. There is no reliable or easy way to confirm this coverage when the patient is admitted. Medicaid and Medicare coverage is determined periodically (weekly or monthly), so the insurance rolls are always changing. It is therefore important that hospitals and other providers of health care obtain accurate, complete and timely information about each patient’s health insurance eligibility.
The admissions clerk can dial the number of the information service or patient’s health care provider and get a verbal confirmation that the insurance is covered. Many hospitals and health care providers also have “POS” terminals (also known as “point of sale”) and/or computers that are able to connect electronically via telephone lines with information providers”, sometimes called clearinghouses, that verify eligibility for health insurance coverage. These techniques, however, require that the clerk admitting a patient decide whether to check for health insurance coverage and take any additional steps to verify. These techniques have the disadvantage that they do not automatically verify insurance eligibility. The admissions clerk may not be able to spend enough time verifying the insurance eligibility of all or some incoming patients if he or she is busy. The billing department of the hospital will have to deal with many issues later when trying to collect fees and costs from the insurance companies.
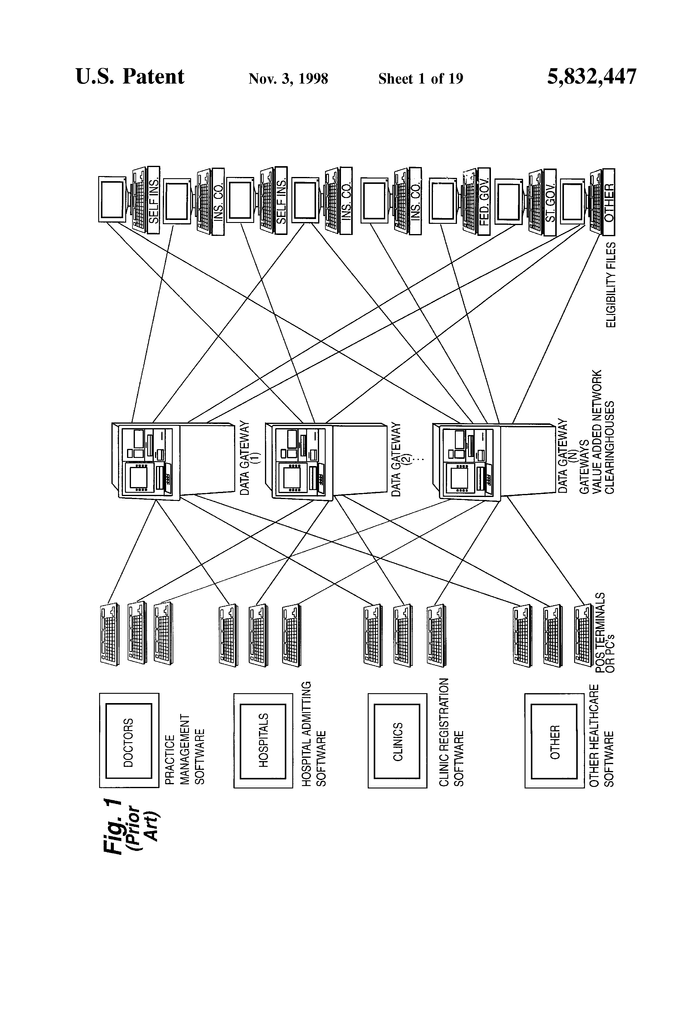
FIG. Figure 1 shows a schematic illustration for a prior art insurance eligibility check “network”. The right side of the figure displays a number of health insurance payers. Some patients are self-insured, through their business, whereas others have health insurance through traditional insurance companies. Some patients are insured by the Federal Government, or by a state government. These insurers can periodically provide eligibility information to value-added networks that are called “data portals”. These data gateways may be called “clearinghouses” because they receive information on insurance eligibility from a variety of health insurers and then make that information available via telecommunications to doctors’ offices and hospitals. Clearinghouses are used to disseminate information about insurance eligibility, but the proliferation of insurers also has led to the proliferation of clearinghouses. It is therefore necessary to get information from data gateway 1 about a certain health insurer, and then to find out eligibility for another health insurer from data gateway 2. The fact that each data gateway has its own proprietary digital communication protocol and can provide POS terminals, or computer software, to access the gateways, makes things even more complex. Many hospital admissions departments have multiple POS terminals. One for each data gateway from which they obtain information about insurance eligibility. One POS terminal must be used to access the data gateway 1 and another POS to access the data gateway 2. It is more difficult for the clerk to verify insurance coverage of patients. “Even when a computer program is used to replace multiple POS terminals the clerk still needs to know how to use several different software packages corresponding with the different clearinghouses.
To add to the complexity, it is not always possible to specify health insurance eligibility with a simple “yes” or “no”. In an increasingly complex world of health insurance eligibility can include qualifications, specific benefits packages, or other important information. Hospitals, for example, need to know if the hospital belongs to the patient’s group of managed care. The hospital will also need to know the co-payment arrangement and the previous health services the patient received under a specific insurance plan. This complicates eligibility verification, making it more difficult and time-consuming. It also makes it less likely to obtain the proper verification at the time of admission.
Many hospitals do not have a reliable procedure or system to verify that each patient who arrives is eligible for insurance coverage. This is due to the pressures and complexities of a hospital’s admissions office, where the primary concern is to treat patients as quickly as possible. The eligibility for health insurance is often not verified until the patient leaves the hospital, or another health care provider. This is done when the hospital, or provider, is trying to collect payment from the patient. It may be impossible to find the patient by this point to get more information about their health insurance. The result is inefficiency, waste of time and effort trying to collect the money from the wrong insurance companies, as well as loss of revenue for the health care provider.
The present invention provides a method and apparatus to solve these and other problems.
The present invention is a method that uses hardware and software in order to capture images of printouts from a computer system used by a healthcare provider. The data in the print image can be used to obtain real-time information on insurance eligibility from payors of health insurance. These electronic eligibility data are received directly from payors or via third-party value added networks, such as clearinghouses. After the image of the patient’s registration is captured, it is separated into data fields. These data fields represent the information needed to register or admit a patient in a healthcare facility. Each group of data pertaining to a patient is treated as a separate transaction. The present invention examines the data items in each transaction to determine whether the patient’s eligibility can be verified. Each transaction is assigned an insurance carrier. The system decides which electronic data sources to use based on the insurance carrier. The system reformats transaction data in order to meet the format requirements of the data source. The system makes a phone call to the data source via modem. The system confirms that the data connection is clear. The system sends to the data source the reformatted transaction data for the eligibility request. The data source transmits the eligibility response data to the system. The system receives the data from the patient’s eligibility response, ensuring that there is no data loss. The system stores data from the transaction of the patient and the data on eligibility. The data is then printed out on a local computer using a printer that has been connected to the system. The system processes the next transaction or waits for the next one to arrive.
According to one aspect of the invention, the health insurance coverage of a patient is automatically verified through input into an automated admissions system. This information relates to a patient who will be admitted to a healthcare provider. The automated admissions system, based on the inputted information generates and transmits digital signals to an printing device, which prints a standard admissions form. According to one aspect of the invention, printed information can be “intercepted” and patient-related information extracted. A digital insurance request message is then generated automatically based on the extracted information. A digital insurance request message is sent in real time over a telecommunications connection, and the digital insurance response message is also received over this link. This response message is used for verifying patient insurance eligibility.
According to another aspect of the invention, information about a patient can be automatically obtained from a computer admissions system. The patient information is used to generate a digital verification message. A digital verification message is sent to a verification institute, and in return a digital response message is received. The received verification response message is used to provide the patient’s healthcare provider with at least some information about the patient’s insurance coverage. These operations are performed in real time (preferably when the patient is admitted, but in any case, before the patient leaves the health care provider).
The following are some of its most advantageous features and benefits:
The present invention provides a system that captures demographic and insurance data from the patient registration software of the provider without the need for programming changes. All other systems require major changes to the provider’s system. The provider information system staff must also be heavily involved.
The system that is provided by this invention has the ability to access and process eligibility transactions in an unlimited number of data sources.
The system provided by this invention automatically reformats patient data into the data set that is required by the source of eligibility data in order to complete a transaction.
The system that is provided by this invention uses patient data to determine the data source with which to communicate to obtain insurance eligibility data in the transaction being processed.
The system that is provided by this invention records and emulates each communication protocol and transaction procedure for each source of eligibility data.
The system that is provided by this invention allows for the storage of transaction data in order to generate reports and provide usage statistics separate from the system used by the health care provider.
The system that is provided by this invention does not require any human interaction in order to complete a transaction.
The system provided by this invention has subroutines that maintain data structures and standards of communication for each source. These subroutines are easily updated by modem in order to add additional sources of eligibility data.
The system provided by this invention determines whether the patient data set has the correct data elements to allow the data source respond to an eligibility query.
The system that is provided by this invention tracks all transactions and provides data on usage to bill the provider, as well as monitor the system.
The system that is provided by this invention can save personnel resources as well as time.
Click here to view the patent on Google Patents.