Invented by Hemanki Kothari, Hyundai Motor Co, Kia Corp
Autonomous cars are equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence algorithms that enable them to navigate roads and make decisions on their own. However, there are situations where the AI system may encounter challenges or face unpredictable scenarios. In such cases, it becomes crucial to have a mechanism that allows a human driver to take control and make decisions.
The market for autonomous car decision override is primarily driven by safety concerns. While self-driving technology has the potential to significantly reduce accidents caused by human error, there is still a level of uncertainty associated with fully autonomous vehicles. The ability to override the AI system and take control in critical situations provides an added layer of safety and reassurance for both passengers and other road users.
Another factor driving the market is the need for regulatory compliance. Many countries and regions have specific regulations in place that require autonomous vehicles to have a mechanism for human intervention. This ensures that the technology is not solely responsible for making decisions that could have significant consequences. As a result, car manufacturers and technology companies are investing in developing and implementing decision override systems to meet these regulatory requirements.
Additionally, consumer preferences play a role in shaping the market for autonomous car decision override. Some individuals may feel more comfortable having the option to take control of the vehicle when needed, rather than fully relying on the AI system. This preference for human intervention can be attributed to factors such as trust, personal choice, and the desire to maintain a sense of control over one’s own safety.
The market for autonomous car decision override is also driven by technological advancements. As self-driving technology continues to evolve, decision override systems are becoming more sophisticated and reliable. These systems are designed to seamlessly transition between autonomous and manual driving modes, ensuring a smooth and safe experience for the driver.
In terms of market players, both traditional automakers and technology companies are actively involved in developing decision override systems. Established car manufacturers are integrating these systems into their autonomous vehicle offerings, while technology companies are developing standalone solutions that can be retrofitted into existing vehicles.
In conclusion, the market for autonomous car decision override is witnessing significant growth due to safety concerns, regulatory requirements, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. As self-driving technology continues to progress, decision override systems will play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of autonomous vehicles. This market presents immense opportunities for car manufacturers, technology companies, and other stakeholders in the automotive industry.
The Hyundai Motor Co, Kia Corp invention works as follows
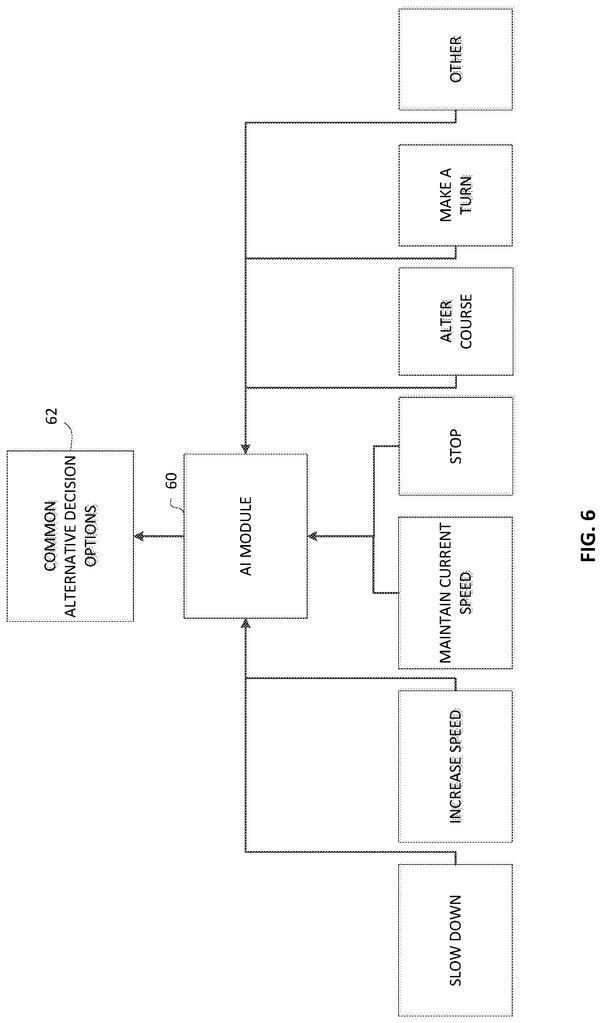
A smart device display that shows an external view of an autonomous vehicle. It also displays the actions the vehicle will take. And it displays the alternative actions an authorized passenger can select to override those actions. This system can also include an artificial intelligence (AI) module that uses machine learning algorithms in order to determine the best alternative vehicle action that the authorized passengers will select for similar situations.
Background for Autonomous car decision override
Currently, passengers in autonomous vehicles do not know what the vehicle will do when it detects a potentially dangerous obstacle such as a vehicle, pedestrian, animal or other object. Moreover, autonomous vehicles do not have visual indicators that alert passengers when the vehicle plans to change speed, stop, or perform another driving maneuver. It can cause anxiety in passengers, as they don’t know what is going to happen next or how they can change the default decisions made by the vehicle. It would be beneficial if the passengers could see or hear the next steps the autonomous vehicle will take.
As autonomous vehicles develop, it is possible that they will no longer have steering wheels, and therefore, the option to override their decisions would not be available. The autonomous vehicle provides passengers with alternative decision options that are made keeping safety in mind. If passengers could select these alternative decisions and override the vehicle’s default choices, it would be very helpful. However, this feature does not currently exist.
The passengers of autonomous self-driving vehicles are currently unable to know what action or next step the vehicle will take until the decision is made. The autonomous vehicle’s passengers do not currently have the ability to alter the default decision of the vehicle. It would be helpful if passengers could choose alternative decisions that override the vehicle’s default decision. However, these features are not available in autonomous self-driving cars.
According to patents already granted, autonomous cars will inform pedestrians on the street about the next steps that the vehicle will take. There is no current feature in the autonomous vehicles that displays the next steps and actions the vehicle will take to passengers inside the vehicle. There is no way for passengers to choose alternative options from the autonomous vehicles that they are presented with, while keeping safety in mind.
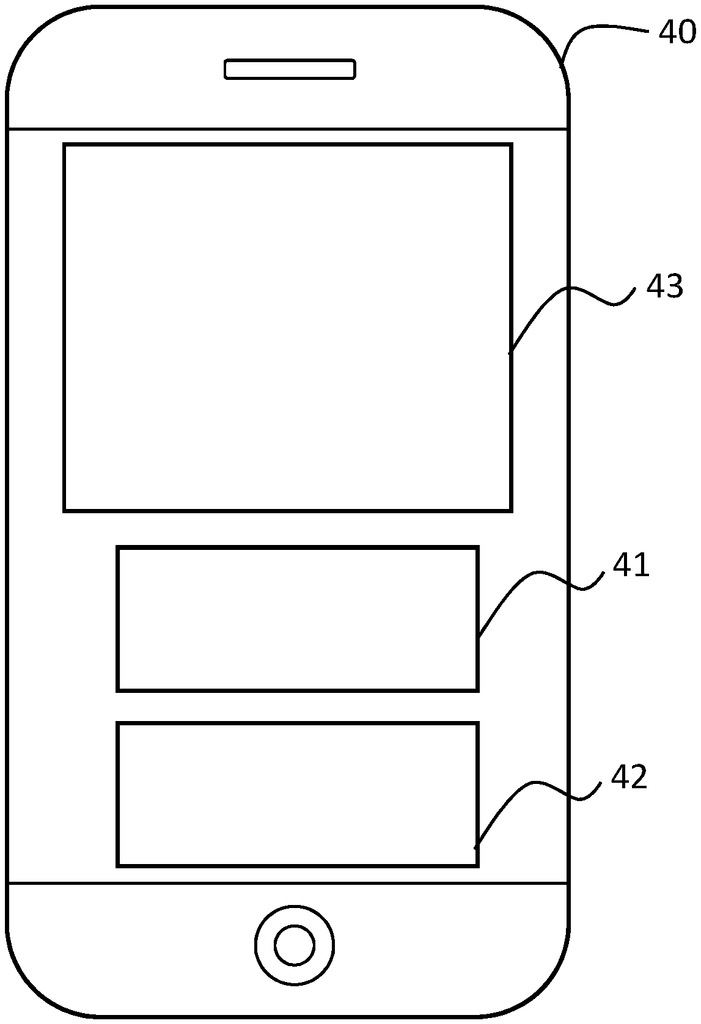
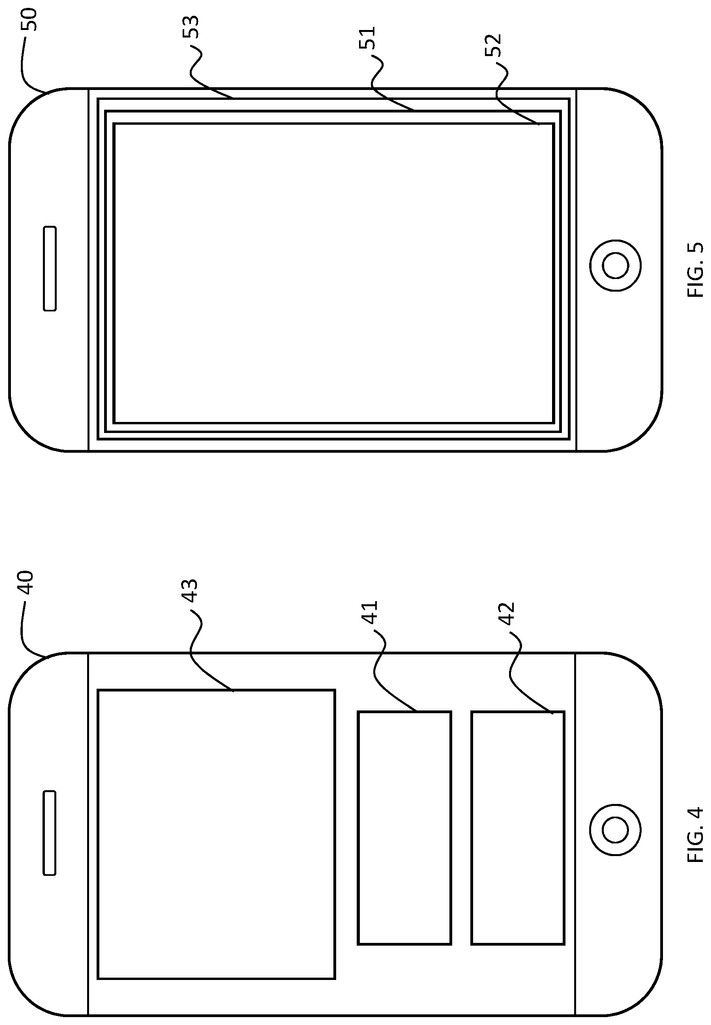
The visual display of an autonomous vehicle is described. The visual display includes three sections: a first section that shows an external view of an autonomous vehicle; a second section that shows the actions the autonomous car will take; and a final section that shows alternative actions an authorized passenger can select to override those actions.
The method is described in further detail as a way to control an autonomous vehicle. The method comprises displaying an exterior view of the autonomous vehicle, displaying the vehicle actions the autonomous car will take, displaying the alternative vehicle action that the autonomous vehicle can take, receiving an authorized passenger’s selection of alternative vehicle acts and overriding vehicle actions by the selected alternative actions.
The description also includes a visual display for an autonomous vehicle. The visual display has two sections: a first section displays the actions the autonomous car will take, and a secondary section displays the alternative actions an authorized passenger can select to override those actions.
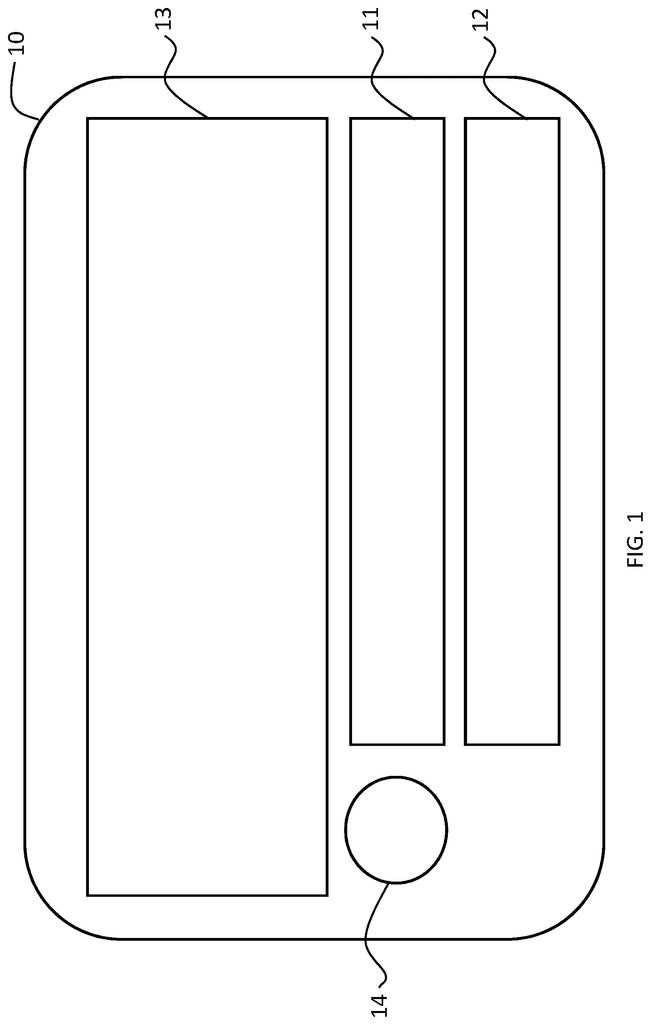
A decision system for an automated vehicle that includes an input sensor that collects information from passengers in order to determine whether a passenger has been authorized and a display that shows alternative vehicle actions an authorized driver of the vehicle can select to override the actions of the vehicle.
A smart device display for an automated vehicle that includes a first section that shows an external view, a section that shows the actions the autonomous car will take and a section that displays alternate vehicle actions.
The smart device display, wherein the first section of the display identifies external hazards based on external view.
The smart device display, wherein the first section of the display shows overlaid simulated directions for navigation based on vehicle actions the autonomous vehicle will undertake.
The smart device display that bases the vehicle’s actions at least t percent on sensor readings from external obstacles.
The smart device display that displays vehicle or sensor malfunctions in either the first or second display sections.
The smart device screen wherein the first display, the second display, and the third display are able to be overlaid one on top of another on the smart display screen.
The smart device display that allows the user to enable or disable the first display, the second display, or the third display displayed on the display screen.
The smart device display that allows the user to choose between slowing down, increasing the speed, maintaining current speed, stopping the vehicle, changing the course or turning the vehicle.
The smart device display that allows the first display, the second display and the third display to be displayed simultaneously on the smart device screen as well the display screen in the autonomous vehicle.
The smart device display that allows the first display, the second display and the third display to be displayed alternatively on the augmented-reality view within the autonomous car, allowing an authorized passenger to choose the alternative vehicle decisions to override autonomous vehicle decisions using the augmented-reality view.
The smart device display that identifies a passenger as an authorized passenger using either a verbal or hand-entered code, or a biometric sensor.
The smart device display that allows a passenger to speak a preset keyword in order to activate an app or system for autonomous vehicles on their device.
The smart device display also includes an artificial intelligence (AI) module that uses the learned alternate vehicle actions in order to present the commonly selected alternative actions to the authorized passengers for similar future situations.
Click here to view the patent on Google Patents.